In the early ‘naughts, people probably noticed as American highways suddenly filled up with wedge-shaped Toyota Priuses.
The harbingers of the alternative fuel revolution touted battery technology as the path to the future. Tesla’s all-electric models have now taken center stage as standard bearers for the eco-friendly.
However, there’s another sustainable fuel source that predates these hybrid and battery-powered technologies: hydrogen.
The first hydrogen-powered car was built all the way back in 1807. It was quite different from the fuel-cell vehicles of today, but the potential of this natural gas has been known to humans for quite some time.
In recent years, many automakers have launched hydrogen fuel-cell vehicles people may not know about. They’re out there, rolling around American streets today. What makes hydrogen special, though, and what is a fuel cell?
Hydrogen as Fuel
Unlike petroleum-derived fuels, hydrogen has the distinct advantage of abundance. It’s the most abundant natural resource on the planet, but it’s usually bonded to some other molecule. Take water, for example, which is two parts hydrogen and one part oxygen.
To extract energy from hydrogen, fuel cells expose it to a platinum catalyst, which pulls the electrons from bonded hydrogen.
These particles provide power for an electric motor and are then rejoined with the hydrogen isotope, as well as oxygen to create water, the only byproduct of the fuel-cell process. So hydrogen is easy to find, generates electricity for power, and the only byproduct it produces is water. It sure sounds better than gasoline at this point.

Where does one go to put hydrogen into their hydrogen-powered car? They would visit a filling station, just like they would for a gasoline-powered vehicle. Instead of gas, though, this one holds chilled compressed hydrogen.
It may not be common knowledge, but a network of hydrogen filling stations is already in place in California, with a handful of other states beginning to follow suit.
A full tank of fuel could be put into a hydrogen fuel cell car in about five minutes, and ranges can be anywhere from 250 to 350 miles, which handily outdoes many electric vehicles.
Fuel-Cell vs. Electric Technology
That all sounds great, but people might wonder where to get a fuel-cell vehicle (FCV). It’s admittedly more difficult to find a manufacturer that offers such a car than to find one that markets hybrid or electric ones.
With the electrification craze taking off recently, it’s correct to assume most manufacturers have placed their bets on that technology. However, FCVs have some distinct advantages that make them attractive alongside their electrified cousins.
Whereas electric cars make great runabouts for zipping up the street to work, FCVs are more efficient highway cruisers. Their longer range and quicker time to fuel up — many electric cars take a half hour or longer — gives them a chance to compete in the long term, and even possibly co-exist with them.
There’s a lack of support outside of California for now, but as has been seen with Tesla’s development of supercharger stations for electric cars, it just takes one big name to get behind the effort and that lack of supply is easily overcome.
Toyota, Hyundai and Audi all have FCVs in some form of production. The Toyota Mirai, which resembles a Prius that swallowed a baby Prius, has sold 6,000 units globally since its introduction — thanks in part to a program to provide buyers with three years of free fuel.
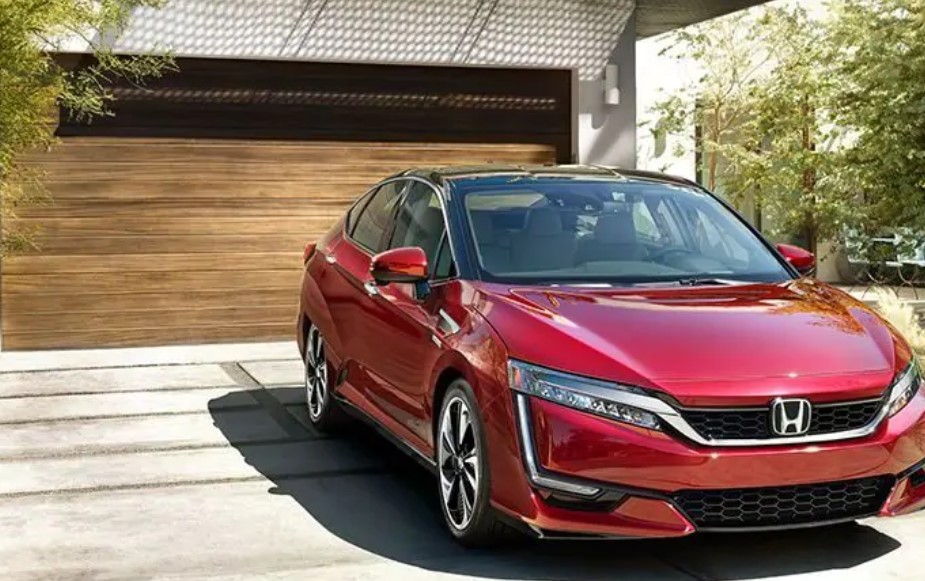
Honda offers an FCV version of the Clarity sedan, and Hyundai offers a hydrogen fuel cell version of its popular Tuscon SUV that’s available through a car rental program. Even Audi has put a foot forward with the H-Tron hatchback, a less mass-market offering but a chance for hydrogen to go a little upscale.
Hydrogen fuel cell cars might not be tomorrow’s vehicle today, but they do have quite a bright future.
With more questions being raised about where all the electricity from EVs is generated and how drivers can dispose of the batteries from Teslas and the like in a sustainable way, hydrogen might have a better chance than people think.
Besides, how cool is water coming out of a tailpipe? That’s something that’s got to be seen to be believed.
Recent Stories
Follow Us On
Get the latest tech stories and news in seconds!
Sign up for our newsletter below to receive updates about technology trends