There’s a case to be made for robotics in healthcare, like in other industries. It’s probably why sales of industrial robots grew by 31% in 2017 over the previous year.
Automation, including some types of robots, has been a part of our supply chains and lifestyles for some time now. With few exceptions, these machines have improved how we manufacture goods and deliver services while creating high-value roles and new jobs in the workforce.
Robotics in healthcare is no different. From the manufacturing and distribution side of things to elder and end-of-life care, robots have a significant role to play in human wellness. Here are a few of those applications.
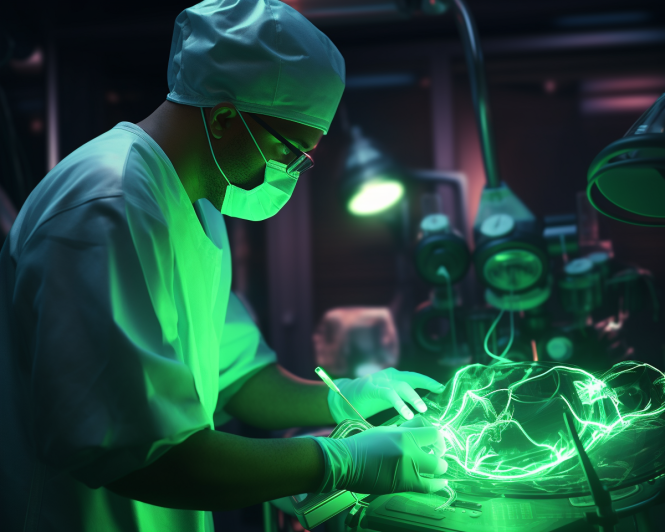
1. Robotic Surgeries
Current robotic surgery systems, including the most famous one, Da Vinci, which received limited FDA approval in 2000, aren’t entirely autonomous.
Even so, these systems provide impressive results and lay the foundation for what’s to come. They feature multiple flexible appendages to position and hold instruments as needed. The robot translates the surgeon’s movements into even more precise ones for delicate operations.
Experts predict we’re many years way from fully autonomous surgery, but robotic assistants help to get us closer. In the meantime, robot-assisted surgery provides other benefits for the surgeon and for the patient, including faster recovery times, smaller incisions, smaller scars, less blood loss and pain, and fewer complications overall.
2. Elder and End-of-Life Care
The aging of the global population is a well-observed phenomenon now, and some countries — like China, Germany, Japan and the U.S. — may be hit especially hard. The looming “elder care crisis” is why these and other countries are increasingly looking to robots to help solve the care gap for their rapidly aging populations.
In Japan alone, robots could help solve a shortfall of some 380,000 specialized aid workers that’s expected to develop by 2025.
From providing companionship and help with everyday tasks to comforting the elderly as they approach the end of their lives, the right robot design could feel like a godsend to somebody living with chronic ailments or uncertainty about the future. Japan already has robots in hospitals performing some of these functions in a limited capacity, and we can likely expect other countries to explore the concept in similar ways.
3. Automated Maintenance and Disinfecting
COVID-19 isn’t the first global pandemic. However, it may be the first such event that permanently normalizes a range of preventive and diagnostic tools, technologies, techniques and methodologies. It could rewrite how we deliver education and healthcare, conduct business and governance, and socialize.
One novel application for robotics in healthcare could be a bright spot — literally — during the pandemic and a source of security for patients and staff alike afterward.
Robots are now helping carry out regular disinfecting efforts at hospitals around the world using flashes of UV light to kill viruses and bacteria. The result is a cleaner facility and one less task left to human fallibility.
Healthcare facilities will probably be home to various robots in the near future, including automated guided vehicles for moving supplies (e.g. towels, linens, PPE) or guiding patients or visitors through buildings.
4. Manufacturing Healthcare Products
Robotic automation is a powerful tool in manufacturing and distribution environments.
For a start, robotic inspection stations equipped with machine vision can spot product defects at a faster rate and with greater accuracy than human beings. In turn, employees can reskill portions of their workforce for more interesting, higher-value work.
These and other repetitive tasks are best left to robots, especially in risk-averse industries like healthcare manufacturing, where lapses in quality assurance can lead to recalls and worse.
Medical devices, implants, wearables, medications and cosmetics products are some of the most highly regulated products on the market today, making them exactly the sort of logistical and quality control challenge that robotic automation was envisioned to solve.
5. Laboratory Assistance
According to recent economic research from Kalorama, robotic laboratory automation systems are on track to become an $8.8 billion industry. There are several reasons for this strong demand, including a shrinking talent pool of qualified lab personnel and higher global demand for laboratory services.
That same Kalorama report finds that around 60% of the ongoing costs in laboratories are due to labor. From sorting and labeling samples to transporting them between analysis stations, there’s plenty of labor happening in the average lab — and plenty that can potentially go wrong.
Robotic laboratory systems automate repetitive tasks such as material retrieval and transportation, cooling or heating materials, shaking, mixing or testing specimens, and tracking each specimen or material as it moves through different processes. The result is faster processing even for large numbers of samples and fewer errors.
Robotics in Healthcare: A Golden Opportunity
The right investment in robotics can improve our manufacturing processes, patient outcomes, work environments and product quality. Robots also require an investment in people — including educational opportunities or reskilling to help employees navigate the automation transition and secure higher-value work.
No matter what, robotics in healthcare is a golden opportunity at a time when the world needs a secure, safe and flexible healthcare infrastructure more than ever.
Recent Stories
Follow Us On
Get the latest tech stories and news in seconds!
Sign up for our newsletter below to receive updates about technology trends